Artificial sweetener Sodium Cyclamate
Sugar is the most prevalent food flavor which is almost everywhere in the food industry. Sugar not only sweetens but also gives a good texture to food ranging from the most traditional candies and beverages to complex condiments and baked goods. As the market progress and consumers look for a better taste, sweetness has been changed into different kinds which include traditional sugar, artificial sweeteners, and natural sweeteners.
Among the artificial sweeteners, saccharin, Sodium Cyclamate and aspartame were the early ones and they were among the first artificial sweeteners. They became a revolutionary breakthrough in the area of food processing. They also mimic sugar’s sweetness, require lesser quantity and have nearly zero calorie content, making them a major progress for diabetics or those living a low-sugar lifestyle.

Sodium cyclamate, also known as sodium cyclohexane sulfonate, is a popular artificial sweetener which is approximately 30 to 50 times sweeter than regular sugar and so only a small amount is needed and this is how the caloric content is reduced in food processing. This is a great benefit for people who wish to manage their energy intake, control hair weight, and regulate their blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, the heat-resistant and storage stability of sodium cyclamates are especially beneficial in baked products and heat-treated foods. Nevertheless, the safety and usage limits of sodium cyclamate and other artificial sweeteners are still governed by food safety agencies in various places in the world.
The history of cyclamate
The discovery of Cyclamate was made in 1937 by Francesco Meglio and Michael Sveda. Cyclamate was used as an alternative to sugar because of sugar rationing during World War II. It was accepted as a food additive in America in 1950.
Within the next few decades, cyclamate was used on a large scale all over the world, particularly in diabetic foods and sugar-free products. Nevertheless, some studies in 1970 reported that cyclamate may be associated with tumors. Nevertheless, the FDA banned the use of cyclamate in foods in the United States in 1970 due to the controversial nature of these studies. Most of the countries reapproved the consumption of CK after decades of further research and review as well as within specific tolerable levels.
Nowadays, cyclamate is mainly applied in soft drinks, candies, bakery products, etc., usually in mixtures with other sweeteners, such as sodium saccharin or aspartame. The worldwide market of cyclamate is anticipated to rise gradually in the years to come.
Application of sodium cyclamate
Sodium cyclamate, as a low-cost sweetener with a taste profile close to sucrose, has been accepted globally almost due to its fairly low price. It is used in many applications and is widely used in virtually all food processing industries, but fundamentally in low-sugar or sugar-free alternative products.
Sodium cyclamate is widely used in the beverage industry in all types of zero-sugar or low-sugar drinks such as carbonated soft drinks, juices, tea beverages and sports drinks. In such products as confectionery and canned fruits, though, sodium cyclamate is frequently used to sweeten, maintaining the original taste of the food, but decreasing the total sugar level. Moreover, sodium cyclamate is a common sweetener in the baking industry, particularly in cookies and other baked goods where it gives long-term sweetness and also remains stable during heat processing. Cyclamic soda also offers an advantageous alternative to sugar when it comes to the preparation of all kinds of condiments such as pickles, which not only taste good but also do not add any extra calories to them.
Safety and Regulation of Sodium Cyclamate
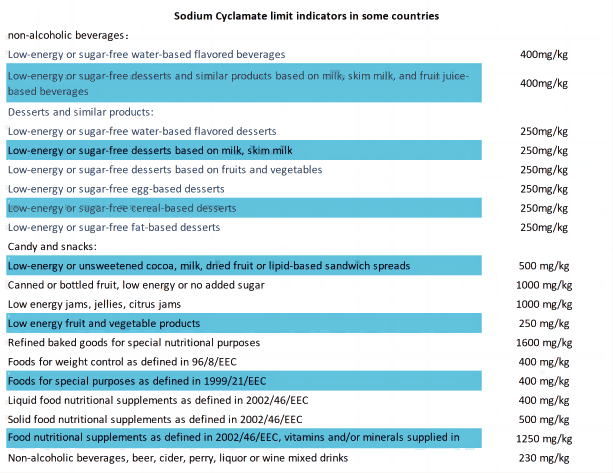
The worldwide disparity in the acceptability of sodium cyclamate is demonstrated by the regulation status of this salt. They have different views. Consumption of sodium cyclamate as a food ingredient has been set through as a safety for more than 50 countries and areas like the EU, the UK, Australia and New Zealand. The FAO/WHO Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) and EFSA have made the unambiguous safety governing the sodium cyclamate, as an artificial sweetener, in non-specific foods and beverages after careful study.
Nevertheless, some countries like the USA and Japan banned sodium cyclamate due to the previous data of experiments which is said to have the fact that it might cause the risk of carcinogenic. Europe has fixed the cyclamate consumption ADI limit for all specific weights and ages which should be not more than 7 mg/kg. These laws prove the point that severe restrictions are taken as to what sodium levels are used in any food product. In China, sodium cyclamate is also controlled in the national food safety standard for food additives.
Concerns about sodium cyclamate safety have always been among the key sticking points in public discussion. A study done in 1969 revealed that a mixture containing materials like sodium cyclamate and saccharin at high dosages could promote bladder cancer. The milestone examination put forth in 1970 increased other people’s worries, too. However, it turned out that in the experiment later done the cyclamate doses which were used had values much higher than those found in human’s exposures to it and there were some more confusing factors.
Furthermore, the cyclamate monkey-study results may range from the short-term to the long-term impression on the safety of humans. The no-case developments for bladder cancer and non-cardiovascular disturbances related to cyclamate, even with very high cyclamate intake, provided another important evidence in favor of the safety of cyclamate. This laboratory outcome thereby implies that sodium cyclamate is potentially safe at an ordinary dosage.
The scope of the investigation has been widened to the possible effects of non-caloric sweeteners on gut microbiota and introduction of likelihood of glucose intolerance. Whilst the issue may be a matter of concern to the scientific community and may raise more questions than answers there is no denying that sequencing the human genome was the most momentous achievement of our time. First studies and reviews demonstrate no health concerns, and therefore current sugar standards are safe for human consumption.
Sodium cyclamate market trend
Several factors constitute the global standing of sodium cyclamate towards sweetener market. The net market value of sweeteners in the world in the year 2022 was $109.4 billion; however, it will be forecasted to reach $113.77 billion in the next year. The share of the market is expected to grow from the 2023 level of $124.97 by 3.7% every year until 2033 equals $164.41 billion.”
This growth trend is mainly driven by the following factors:
- Increasing health awareness:
The technological advancements in the food industry have led to the development of new products that are aimed at curbing consumers’ excessive sugar intake as well as catering to the growing demands for no-calorie or few-calorie sweeteners. Today, diabetes and obesity rates are globally rising; therefore, when governments and consumers choose to reduce sugar intake, it is a sole priority for them. The use of sweeteners is mentioned as one of the options for avoiding these problems, which results in the reduction of calorie and sugar intake.
- Expanding applications:
As well as in the food business, this is not limited to the area of sweeteners which are now being used in the personal care, pharmaceutical, dietary and other types of supplements industries. The rising affluence of middle classes among the developing nations is, moreover, characterized by the increased consumption of sweeteners that is a whipsaw of changing global diet trends.

The important market movement here is that a bunch of countries are imposing taxes on sugar to control high levels of obesity. The WHO, for the first time, has come up with a worldwide guide on sugar taxes. In a minimum of 85 countries, sugar taxes are already in existence. Such tax measures are considered to be among the most powerful health-promotion instruments as they can be life-saving, prevent diseases and disease mainstreaming, and ultimately contribute to funding universal health coverage.
Sodium Cyclamate is the second most important additive in the globe in the field of food industry as to its features of being cheaply priced and highly flavored artificial sweetener. The fact that more and more consumers are increasingly conscious of their health, and the expanding range of applications of low-calorie ‘zero’ sweeteners give the market a lot of prospects for users of Sodium Cyclamate. Nevertheless, the expansion of the middle class in developing countries fosters the location of Sodium Cyclamate into new areas of application, for instance, cosmetology and pharmaceutical industry, and so on, and there is a very brilliant future for the Sodium Cyclamate market.
However, Sodium Cyclamate faces a tussle against natural sweeteners, and difficulty in the countries and regions in which restrictions are imposed, and issues of consumer safety caused by that. As a high-standard supplier of Sodium Cyclamate, Mondstar assumes the tasks of product quality and service improvement, and meeting the demands of local market; and its active promotion of Sodium Cyclamate for its image building. The world food additives market offers great potential, and we intend to develop partnerships with new customers and markets to capture this opportunity and extend the use of Sodium Cyclamate worldwide. The present situation encourages us to stimulate growth in the industry by introducing new product to the global market.
Related Posts:
1. What does carboxymethyl cellulose use in food?
2. Do you really know about food additives?
